|
|
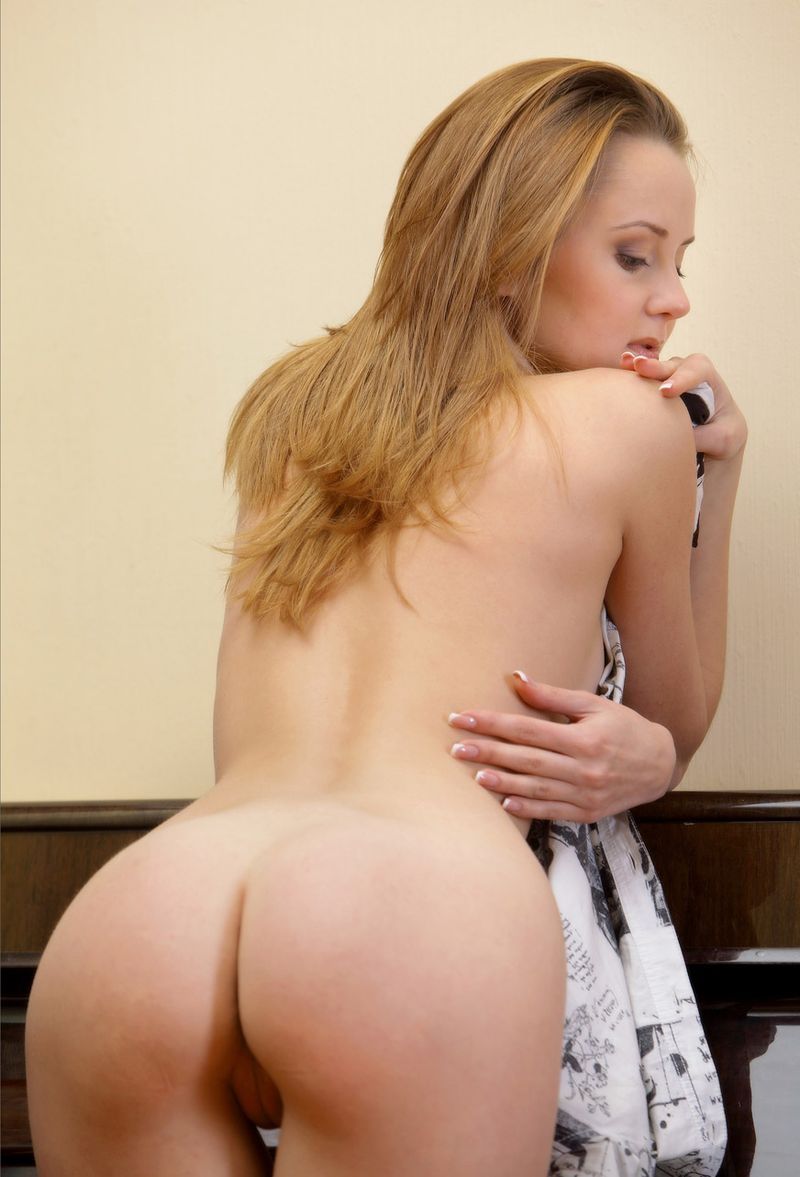
Young Dark Blonde Girl Reveals At The Piano
|
Cristofori's new instrument remained relatively unknown until an Italian writer, Scipione Maffei, wrote an enthusiastic article about it (1711), including a diagram of the mechanism. This text was widely distributed, and most of the next generation of piano builders started their work because of reading it. One of these builders was Gottfried Silbermann, better known as an organ builder. Silbermann's pianos were virtually direct copies of Cristofori's, with one important addition: Silbermann invented the forerunner of the modern damper pedal, which lifts all the dampers from the strings at once.
Silbermann showed Johann Sebastian Bach one of his early instruments in the 1730s, but Bach did not like it at that time, claiming that the higher notes were too soft to allow a full dynamic range. Although this earned him some animosity from Silbermann, the criticism was apparently heeded. Bach did approve of a later instrument he saw in 1747, and even served as an agent in selling Silbermann's pianos.
Piano-making flourished during the late 18th century in the Viennese school, which included Johann Andreas Stein (who worked in Augsburg, Germany) and the Viennese makers Nannette Streicher (daughter of Stein) and Anton Walter. Viennese-style pianos were built with wood frames, two strings per note, and had leather-covered hammers. Some of these Viennese pianos had the opposite coloring of modern-day pianos; the natural keys were black and the accidental keys white. It was for such instruments that Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart composed his concertos and sonatas, and replicas of them are built today for use in authentic-instrument performance of his music. The pianos of Mozart's day had a softer, more ethereal tone than today's pianos or English pianos, with less sustaining power. The term fortepiano is nowadays often used to distinguish the 18th-century instrument from later pianos.
In the period lasting from about 1790 to 1860, the Mozart-era piano underwent tremendous changes that led to the modern form of the instrument. This revolution was in response to a consistent preference by composers and pianists for a more powerful, sustained piano sound, and made possible by the ongoing Industrial Revolution with technological resources such as high-quality steel, called piano wire, for strings, and precision casting for the production of iron frames. Over time, the tonal range of the piano was also increased from the five octaves of Mozart's day to the 7¼ or more octaves found on modern pianos.
|
|